course:nctu-高等unix程式設計:chapter7
目錄表
Process Relationship
0x00 Outline
- Logins
- Process groups
- Sessions
- Controlling terminal
- Job control
- Shell execution of programs
- Orphaned process groups
- FreeBSD Implementation
0x01 Logins
Boot Process
- /sbin/init 是系統開起來之後的第一支程式
- 是所有 process 的 parent,PID 為 1
BSD Terminal Logins
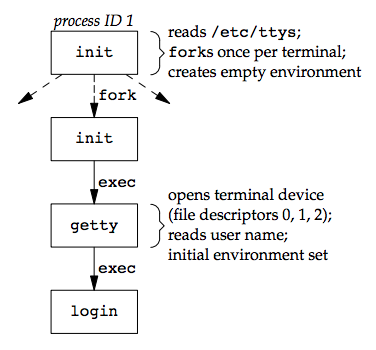
/etc/ttys檔案中對每個 terminal device 都有一行對應的設定,包括 device name 和相關參數這些設定會傳送給getty這隻程式- 當系統啟動後,kernel 會產生 init process(pid 1),init process 會去讀取
/etc/ttys,並對於每個允許的 login terminal 執行 fork,並跑 exec 執行 getty
- 上面所有的 process ruid & euid 為 0,皆擁有最高權限,而除了最原始的 init 外,其他 process 的 ppid 為 1
initexecutegettyprogram with empty environmentgetty呼叫open來開啟 terminal device 進行讀寫, file descriptor 0,1,2 被配置在 device 上- 接著
getty會產生輸出如 login: 並等待 user name 輸入 - 收到 username 後
getty執行login如下
execle("/bin/login", "login", "-p", username, (char *)0, envp);
- 因為
init時 environment 是空的,getty 在這邊會為login產生 envirement(envp argemnet), -p flag 用來告訴login保留傳遞過去的 enviroment login接下來會- 呼叫
getpwnam取得 user's password file entry - 呼叫
getpass顯示 Password: 提示使用者輸入,並讀取輸入的密碼 - 呼叫
crypt來加密使用者輸入的密碼,和從 password file entry 中的 pw_passwd 欄位做比對 - 對傳統 UNIX ,如果登入失敗,
login會呼叫 exit 帶參數 1,這個 terminate 會通知給 parent(init),parent 會再做一次 fork、exec、getty 對這個 terminal 重複一次上述流程 - 然而現今 UNIX 有許多不同的登入驗證方式,細節可以參考 PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules)
- 接著如果登入成功,
login會- chdir 到我們的家目錄
- 對 terminal chown,讓我們擁有這個 terminal device
- 改變 terminal device 的存取權限,讓我們可以 read from 和 write to terminal device
- 呼叫
setgid和initgroups,設定我們的 group id - 初始化 environment,HOME、SHELL、USER;LOGNAME、PATH
- 改變 user 的 uid,並調用 user shell
execl("/bin/sh", "-sh", (char *)0);
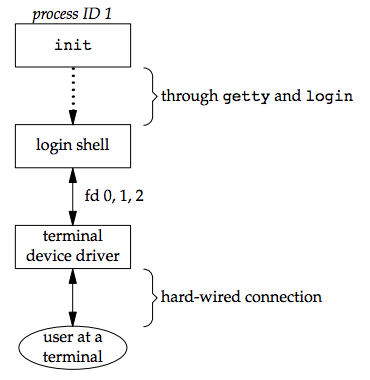
login可選擇印出 message-of-the-day(motd),check new mail 或執行其他工作- 至此,login shell 就跑起來了,他的 parent process 為 init,init 會發出 SIGCHID signal,並為這個 terminal 重複一次整個程序
- shell 的 file descriptors 0,1,2 會被設置到 terminal device 上
- 接著 login shell可以調用各自的 start-up file (.profile or .cshrc, .login)
BSD Network Logins
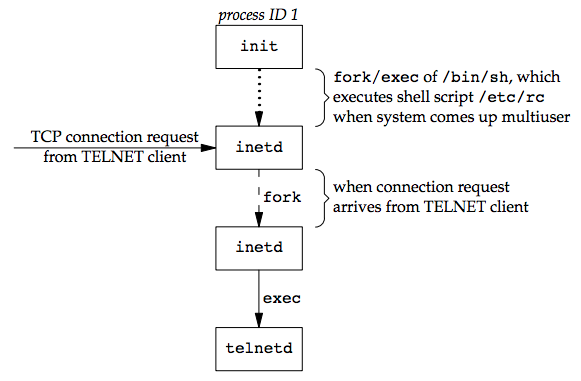
- 為了使 terminal login 和 network login 能用一樣的 program 來 login,software drivcer 會呼叫 pseudo terminal 來將 network login 模擬成 terminal login
- 在 BSD 中
inted這隻 process 會等待處理大多數的網路連線 - 當系統啟動時,
init會調用一個 shell 來執行 /etc/rc 這個 shell script,他會啟動 inetd 和其他 daemon,當 /etc/rc 結束後,inetd的 parent會變成init inetd會等待 TCP/IP 連線,當有連線請求時,inetd會 fork,並 exec 執行對應的程式
- 當
inetd收到連線請求後(以 telnet 為例)- parent(telnetd) 會處理網路連線上的 communication
- child 呼叫 exec 執行
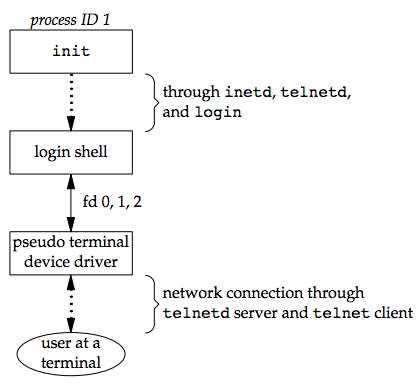
login - parent 和 child 透過 pseudo terminal 連接 ,child 的 file descriptors 0,1,2 會被設置到 pseudo terminal
- 如果登入成功後,後續和 terminal login 相同
0x02 Process Groups
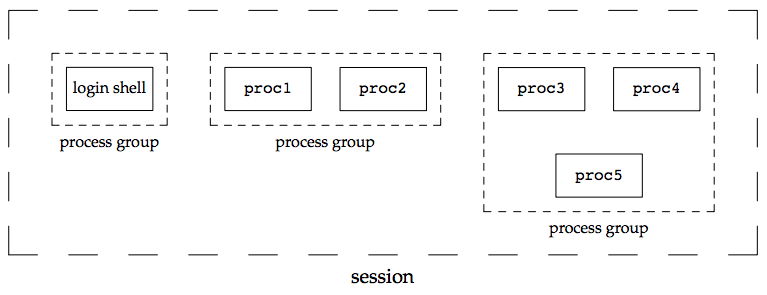
process group
- 每個 process 會屬於一個 process group
- process group 是一個或多個 processes 的集合,可以從同一個 terminal 收到 signal
- process group 有自己的 pgid,可以用
pid_ttype 儲存 - 可以用 pgid 對整個 group 發出 signal 或 waitpid
#include <unistd.h> pid_t getpgrp(void); /* Returns: process group ID of calling process */ pid_t getpgid(pid_t pid); /* Returns: process group ID if OK, −1 on error */
- 如果 getpgid 的引數 pid 為 0,則會回傳 calling process 的 pgid
- getpgid(0); 等同於 getpgid();
- 每個 process group 可以有一個 process group leader,此 group 的 pgid 為 process group leader 的 pid
process group lifetime
- 起始於 group 被創造的時候
- 結束於 group 最後一個 process terminate 或離開 group,跟 process group leader 存不存在無關
create or join a process group
#include <unistd.h> int setpgid(pid_t pid, pid_t pgid); /* Returns: 0 if OK, −1 on error */
- if pid==pgid, 該 pid 的 process 成為 process group leader
- if pid==0, 則會使用 caller 的 pid
- if pgid==0, 則 pgid=pid
- setpgid 的限制
- 一個 process 只能對自己或是其 child 進行 setpgid
- 當某個 child 呼叫了 exec function 後便無法對其 setpgid
- use setpgid
- 當 fork 之後 parent 會對 child setpgid
- 而 child 自己也會在 setpgid 一次
- 雖然看起來多餘,但可以保證 child 被加入適當的 process group\
0x03 Sessions
Session
- session 是一或多個 process group 的集合
- 以 pipe 連接的 process 會放置在同一個 process group
proc1 | proc2 & proc3 | proc4 | proc5
create a session
#include <unistd.h> pid_t setsid(void); /* Returns: process group ID if OK, −1 on error */
- 如果 calling process 不是 process group leader,則 setsid 會創造一個新的 session
- calling process 會成為新 session 的 session leader,這個 process 是 session 中的唯一 process
- calling process 也會成一個新 process group 的 process group leader,新的 process group 的 pgid 會為 calling process 的 pid
- 這個 process 不會有 controlling terminal,如果在呼叫 setsid 前有 controlling terminal,他們的關聯會結束
- 如果 calling function 已經是 process group leader,則 setsid 會 return error
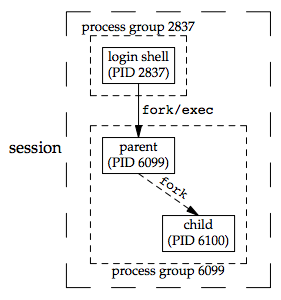
- 確認 setsid 不是回傳 error,一般會呼叫 fork,之後 parent 結束,而child 呼叫 setsid,child 的 pgid 從 parent 繼承而來,而 fork 後 child 會有新的 pid,此保證 child 不會成為 process group leader
get the current session id
#include <unistd.h> pid_t getsid(pid_t pid); /* Returns: session leader’s process group ID if OK, −1 on error */
- 如果引數 pid 為 0,回傳 calling process 的 session leader 所屬的 pgid
- 基於安全,有些實作會禁止 caller 對和自己屬於不同 session 的 pid 使用 getsid
- session id 為 session leader 的 pid
- 當使用者 login 之後, session leader 通常為 shell
0x04 Controlling Terminal
controlling terminal
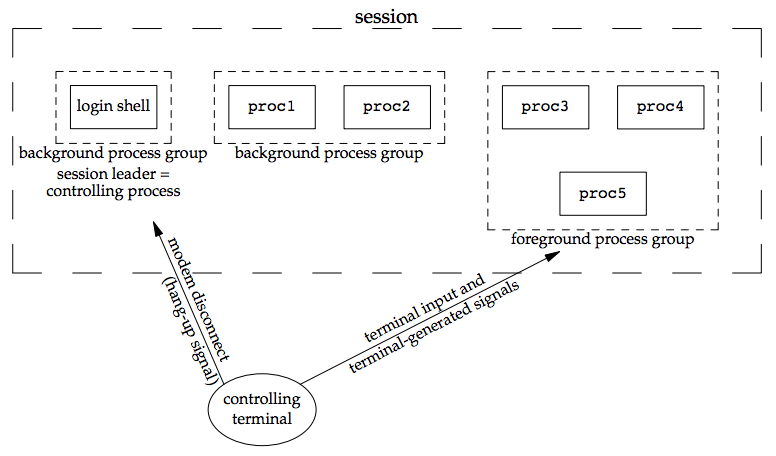
- 一個 session 可以有一個 controlling terminal,通常是 terminal device 或 pseudo terminal device
- session 可以建立和 controlling terminal 的連線,稱為 controlling process
- session 中可以有一個 foreground process group 和多個 background process groups
- 如果 session 有 controlling terminal,則必有一個 foreground process terminal,其他則為 background process groups
- 當我們按下 terminal 的 interrupt key(Ctrl-C) 或 quit key(Ctrl-Backslash),SIGINT/SIGQUIT signal 會被發送給 foreground process group 中的所有 processes
- 如果 network disconnect 被 terminal interface 偵測到,SIGHUP signal 會被發送給 controlling process(session leader)
tcgetpgrp, tcsetpgrp and tcgetsid function
#include <unistd.h> pid_t tcgetpgrp(int fd); /* Returns: process group ID of foreground process group if OK, −1 on error */ int tcsetpgrp(int fd, pid_t pgrpid); /* Returns: 0 if OK, −1 on error */
- The function
tcgetpgrpreturns the process group ID of the foreground process group associated with the terminal open on fd. - 如果 process 有 controlling terminal, 則 process 可以呼叫
tcsetpgrp來將 foreground process group id 設成 pgrpid - 這兩個 function 通常被 job-control 呼叫
#include <termios.h> pid_t tcgetsid(int fd); /* Returns: session leader’s process group ID if OK, −1 on error */
- 應用程式若要管理 controlling terminal 可以使用
tcgetsid來取得此 controlling terminal 的 session leader 的 sid
0x05 Job Control
job control
- 可以讓單一個 terminal 跑多個工作,並決定哪些要在 foreground 那些在 background
- 需要三個條件支援
- Shell support
- terminal driver in kernel support
- kernel must support certain job-control signals
- job 是一系列 process 的集合,通常是 pipeline 的 processes
- terminal driver 會接收的一些訊號
- SIGINT: generated by the interrupt character (typically DELETE or Control-C)
- SIGQUIT: generated by the quit character (typically Control-backslash)
- SIGTSTP: generated by the suspend character (typically Control-Z)
- 在 background 的 process 預設是無法處理 SIGTTIN,像
cat > test.tmp &在 background 就會 stop,直到使用fg將 process 帶回到 foreground ,process才會收到 SIGCONT signal 繼續讀取使用者輸入 - 在 background 的 process 預設可以處理 SIGTTOU ,用
stty tostop可以 disable background output - 可以使用 Ctrl-Z 發送 SIGTSTP signal 停止執行中的 foreground process
0x06 Shell Execution of Program
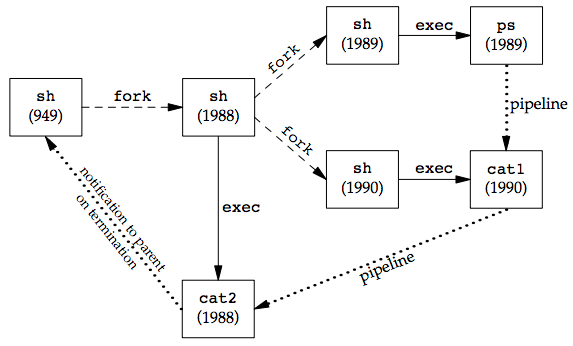
$ ps -o pid,ppid,pgid,sid,comm | cat1 | cat2 PID PPID PGID SID COMMAND 949 947 949 949 sh 1988 949 949 949 cat2 1989 1988 949 949 ps 1990 1988 949 949 cat1
- 根據不同 OS 或 shell 實作方式可能不同
0x07 Orphaned Process Group
orphaned process group
- 一個 process 若他的 parent 已經 terminate,被 init 接手則此 process 稱為 orphaned
- 整個 process group 可能成為 orphaned process group
- 若一個 process group 中所有 process 的 parent 皆在跟自己相同的 process group 或是不同 session 的其他 process group,則此為 orphaned process group
- 反之若 process group 中有一 process 的 parent 為同 session 但不同 process group,則此 process group 就不是 orphaned
0x08 FreeBSD Implementation
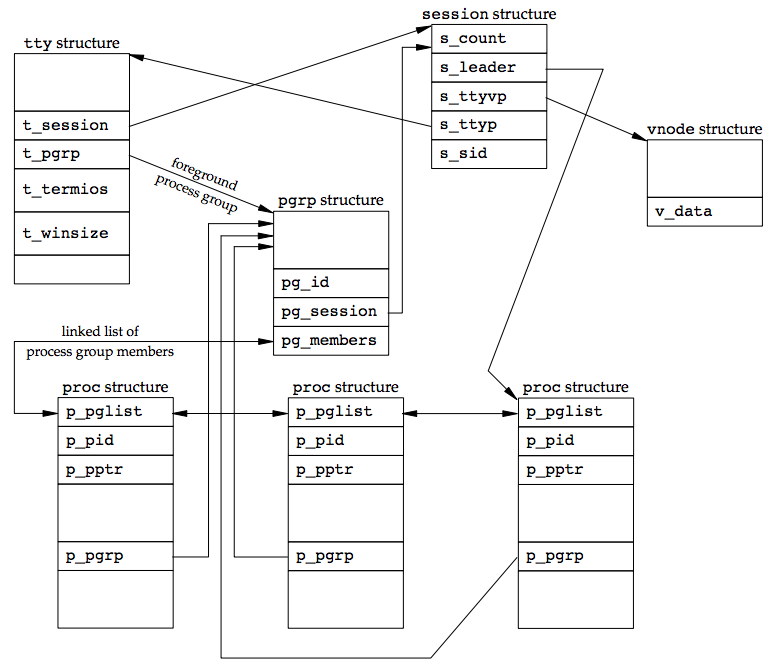
- session structure 會在每次 setsid 被呼叫時配置給每個 session
- s_count: session 中 process groups 的數量,當被減至 0 時, structure 可被釋放
- s_leader: 指向 session leader 的 proc structure
- s_ttyvp: 指向 controlling terminal 的 vnode structure
- s_ttyp: 指向 controlling terminal 的 tty structure
- s_sid: session ID
- 當
setsid被呼叫時,新的 session structure 被配置在 kernel 中- s_count 被設為 1
- s_leader 會指向 calling process 的 proc structure
- s_sid 被設成 calling process ID
- 因為 new session 沒有 controlling terminal,s_ttyvp and s_ttyp 被設為 NULL
- tty structure 包含在 kernel 中,用於 terminal device 和 pseudo terminal device
- t_session: 指向擁有這個 terminal 為 controlling terminal 的 session structure,這個指標被 terminal 用來 terminal 發送 hangup signal 給 session leader.tty 和 session struction 互相指向對方
- t_pgrp 指向 foreground process group 的 pgrp structure,這個欄位被 terminal driver 用來發送 signal 給 foreground process group,有三種特殊字元訊號
- interrupt
- quit
- suspend
- t_termios 是一個 structure 包含此 terminal 的所有 special characters 和 related information,像是 baud rate, 是否允許 echo 等
- t_winsize 是一個 winsize structure 包含目前 terminal window 的 size,當 terminal window 的大小改變時,SIGWINCH signal 會被發送給 foreground process group.
- kernel 藉由 session struction 中個欄位的指標找到特定 session 的 foreground process group
- Follow s_ttyp of the session structure to get to the tty structure (controlling terminal)
- Follow t_pgrp of the tty structure to get to the pgrp structure (foreground process group)
- pgrp structure 包含了特定 process group 的資訊
- pg_id: process group ID.
- pg_session: 指向此 process group 所屬 session 的 session structure
- pg_members: 指向一個 list 包含了此 process group 中成員的 proc structures,proc structure 中的 p_pglist structure 是雙向鏈結串列,指向 process group 中前一個和後一個 process
- vnode structure 在 controlling terminal device 開啟時被配置,所有指向 /dev/tty 的參考都會通過這個 vnode structure
0x09 參考資料
course/nctu-高等unix程式設計/chapter7.txt · 上一次變更: 由 127.0.0.1