目錄表
Files and Directories
0x00 Outline
- Introduction
- File Information
- File Permissions
- File Systems
- Directory Operations
- Device Special Files
0x01 Introduction
File Name
- 檔名可以是除了 slash (/) 和 null (\0) 的所有字元
- 檔名長度上限一般是 255 chars (PATH_MAX constant)
- 每個資料夾必定包含兩個檔案
.: 表示當前目錄..: 表示上層目錄
- 檔名編碼由 user terminal 決定,和檔案內容編碼無關
Path Name
- 絕對路徑: 由斜線開頭,從根目錄開始表示
- 相對路徑: 不由斜線開頭,從當前目錄開始表示
Directory
- Working Directory
- 每個 Process 都有自己的 Working Directory
- 又稱 current working directory
- 可以用
chdir指令改變
- Home Directory
- 使用者登入時的預設 Working Directory
- 記錄在
/etc/passwd檔案中
0x02 File Information
stat, fstat, lstat Functions
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf); int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ struct stat { dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */ blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ };
- 這些函式主要會回傳關於檔案的資訊
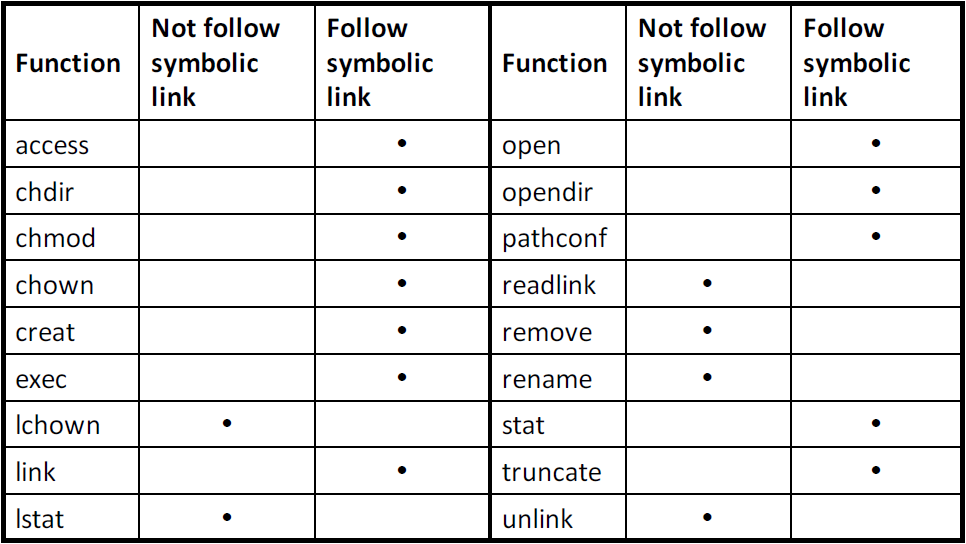
stat和lstat基本上相似,主要差別在stat會跟隨 symbolic link 顯示檔案資訊,lstat則不跟隨 symbolic link,而是顯示 symbolic link 本身資訊fstat則是在參數部分使用 file description,不同於stat和lstat使用路徑,fstat可以取得開啟中的檔案資訊
Common File Information
- File type and permissions
- Number of hard links
- User ID and group ID
- Device number (of the containing file system)
- Device number for special files
- File size
- Block size and number of used blocks
- Timestamps: access, modification, and change
File Types
- Regular file
- Directory file
- Block special file (usually use in device drivers)
- Character special file
- FIFO (named pipe)
- Socket (UNIX socket)
- Symbolic link
0x03 File Permissions
這邊可以先參考 SUID & SGID in UNIX 這篇
#include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> int setuid(uid_t uid); int setgid(gid_t gid); /* Return 0 if OK, -1 if error */
程式在執行時可以透過 setuid, setgid function 來改變 euid, egid
File Access Permissions
- access 需要 execute permissions
- open file for read 需要 read permissions
- open file for write or truncate 需要 write permission
- delete an existing file in a directory 只需要對資料夾有 write and execute permissions
- executable file 需要 execute permission
File access test precedence
- If the EUID of the process is 0, access is allowed
- If the EUID of the process equals the owner ID of the file, access is allowed if the appropriate user access permission bits are set
- If the EGID or supplementary GIDs of the process equals the group ID, access is allowed if the appropriate group access permission bits are set
- If the appropriate other access permission bits are set, access is allowed
符合四項中的其中一項即有存取權限
Ownership of New Files and Directories
- 新檔案的 user ID 會設置成創造檔案的 process 的 EUID
- 新檔案的 group ID 可能被設置成:
- The EGID of the creating process
- The GID of the parent directory
- GID 部分是依照 OS 實作情況決定
- FreeBSD 5.2.1/Mac OS X 10.3 – by the parent directory
- Linux – depends on a mount option (grpid)
- If grpid is set or directory has SGID – by the parent directory
- Otherwise – by the EGID of the creating process
access Function
#include <unistd.h> int access(const char *pathname, int mode); /* Return 0 if OK, -1 on error */
- 可以用來檢查 process 對某檔案是否有存取權限
- mode 可以用 bitwise OR 連接屬性
- R_OK, W_OK, X_OK, F_OK 這幾個 mode 分別可以用來檢測讀, 寫, 執行權限和檢測檔案是否存在
- 此函式是以 real UID, real GID 去檢測,而 open 函式是以 euid, egid 去開檔,所以可能發生 access 顯示無權限,但 open function 可用的情況
- 不跟隨 symbolic link
- a.out
#include "apue.h" #include <fcntl.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) err_quit("usage: a.out <pathname>"); if (access(argv[1], R_OK) < 0) err_ret("access error for %s", argv[1]); else printf("read access OK\n"); if (open(argv[1], O_RDONLY) < 0) err_ret("open error for %s", argv[1]); else printf("open for reading OK\n"); exit(0); }
$ ls -l a.out -rwxrwxr-x 1 sar 15945 Nov 30 12:10 a.out $ ./a.out a.out read access OK open for reading OK $ ls -l /etc/shadow -r-------- 1 root 1315 Jul 17 2002 /etc/shadow $ ./a.out /etc/shadow access error for /etc/shadow: Permission denied open error for /etc/shadow: Permission denied $ sudo su - become superuser Password: enter superuser password # chown root a.out change file's user ID to root # chmod u+s a.out and turn on set-user-ID bit # ls -l a.out check owner and SUID bit -rwsrwxr-x 1 root 15945 Nov 30 12:10 a.out # exit go back to normal user $ ./a.out /etc/shadow access error for /etc/shadow: Permission denied open for reading OK
umask Function
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> mode_t umask(mode_t mask); /* previous file mode creation mask */
- sets the calling process's file mode creation mask
- mode 可用選項有 S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH 分別代表 user, group, other 的 read, write 權限
- umask 一般的預設值為 S_IWGRP | S_IWOTH (022)
- 假設 create 使用了 RWRWRW 權限 (666),則預設 umask (022),最後結果為 0666 & ~022 = 0644
#define RWRWRW (S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|S_IRGRP|S_IWGRP|S_IROTH|S_IWOTH) int main(void) { umask(0); if (creat("foo", RWRWRW) < 0) err_sys("creat error for foo"); umask(S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH); if (creat("bar", RWRWRW) < 0) err_sys("creat error for bar"); }
$ umask // first print the current file mode creation mask 002 $ ./a.out $ ls -l foo bar -rw------- 1 sar 0 Dec 7 21:20 bar -rw-rw-rw- 1 sar 0 Dec 7 21:20 foo $ umask // see if the file mode creation mask changed 002
Set File Modes and Ownerships
#include <sys/stat.h> int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode); int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
- 用來改變檔案權限
- 不跟隨 symbolic link
- mode:
- S_ISUID (4000): set-user-ID
- S_ISGID (2000): set-group-ID
- S_ISVTX (1000): sticky bit
- S_IRUSR (0400): read by owner
- S_IWUSR (0200): write by owner
- S_IXUSR (0100): execute/search by owner
- S_IRGRP (0040): read by group
- S_IWGRP (0020): write by group
- S_IXGRP (0010): execute/search by group
- S_IROTH (0004): read by others
- S_IWOTH (0002): write by others
- S_IXOTH (0001): execute/search by others
#include <unistd.h> int chown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group); int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group); int lchown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group); /* Return 0 if OK, -1 on error */
- chown 不跟隨 symbolic link, lchown 跟隨 symbolic link
0x04 File Systems Files
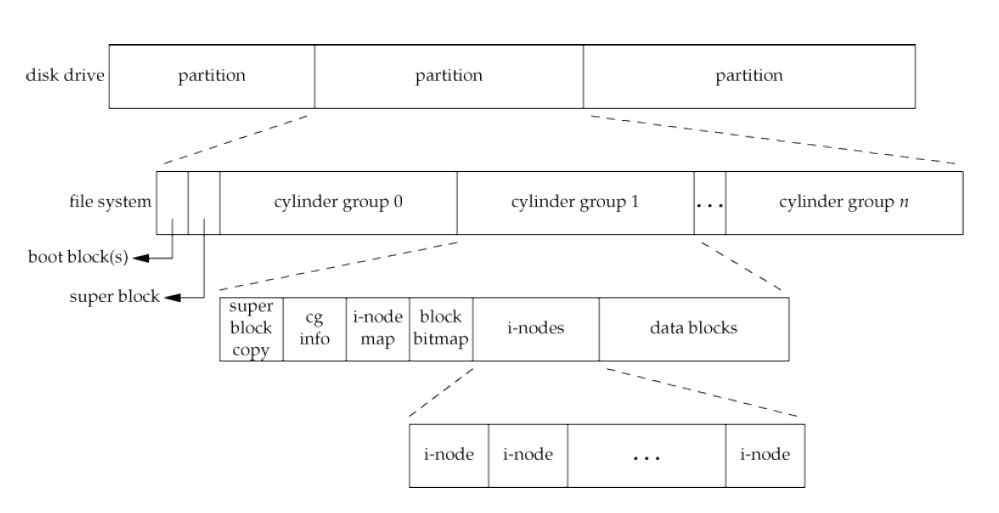
Cylinder Group's i-nodes and Data Blocks
- super block copy: 紀錄 block, i-nodes 的總量、已用數量、未用數量
- i-node map: 紀錄那些 i-node index 是空的
- block bitmap: 紀錄那些 block 是空的,哪些是可用的
- i-node: 紀錄檔案的資訊,如: type, permission, data blocks, timestamps, reference counts 等
- i-node 通常會以正整數做 index
- 有些 i-node number 有特別意義
- 0: reserved, or does not exist
- 1: list of bad/defective blocks
- 2: root directory of a partition
- data blocks: 檔案內容真正存放的地方
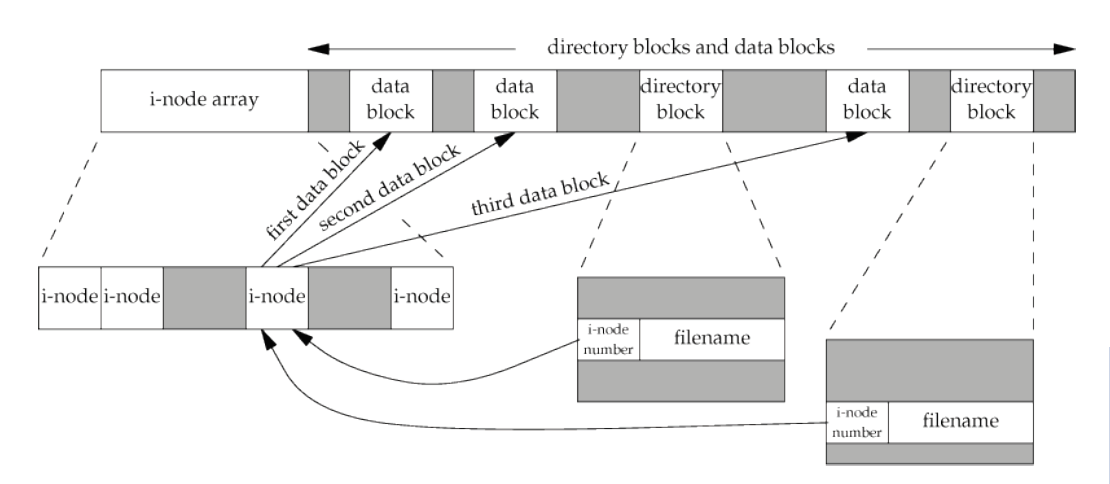
i-node 可被多個 entry 指到
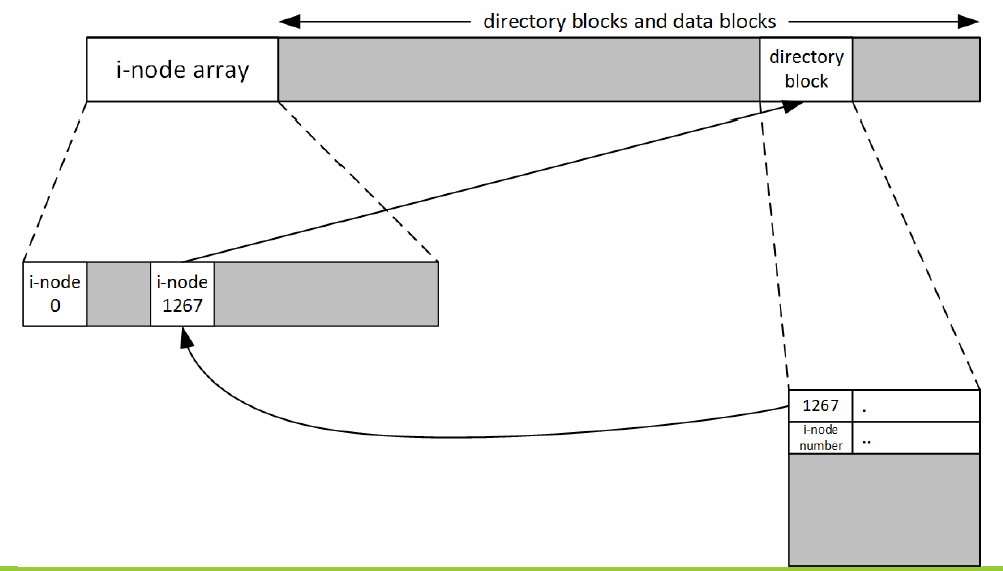
建立資料夾前的 i-node 示意圖:
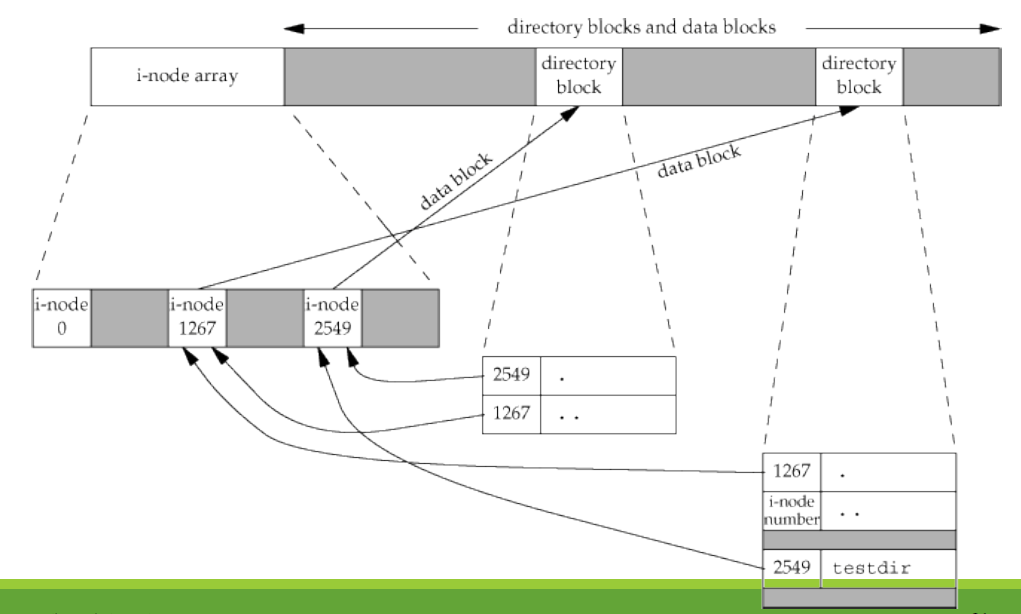
建立資料夾後的 i-node 示意圖:
- 建立新資料夾產生新的 i-node 2549,其中紀錄了 directory block 資訊
- directory 中紀錄了新目錄中的當前目錄 (.),指向自己的 i-node 跟上層目錄 (..) 指向父資料夾的 i-node
- 父資料夾的 directory block 產生了新的資料內容,即為我們建立的 testdir,指向 i-node 2549
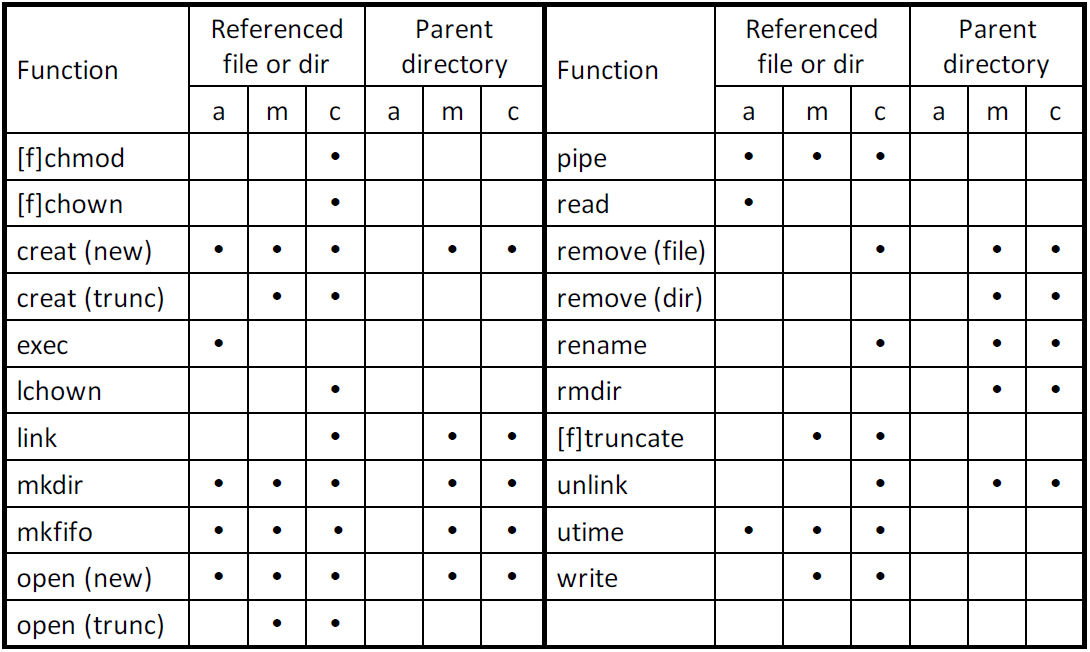
Reference Counts
- 表示指向這個 i-node 的數量
- 剛建立的檔案 reference count 為 1,是檔案所在的資料夾指過來的
- 剛建立的資料夾 reference count 為 2,是資料夾中當前目錄(自己指向自己) 和上層目錄指過來的
- link(2) 會增加 reference count,是 hard-link,必須在同一個 partition
- unlink(2) 則會減少 reference count
#include <unistd.h> int link(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath); int unlink(const char *pathname); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ #include <stdio.h> int remove(const char *pathname); int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */
Relevant Commands
ls -l: long listing format, check the reference countls -ls: show file sizes in 1KB blocksls -li: show i-node numbers
Symbolic links
- 又稱 soft-links
- ln(1) command
- symbolic link 的大小是目標檔案的檔名長度
- soft-links 可指向一個不存在的檔案
- soft-links 可指向任何檔案格式
- hard link 只能指向 regular file,且不可跨分割區
#include <unistd.h> int symlink(const char *actualpath, const char *sympath); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ ssize_t readlink(const char *path, char *buf, size_t bufsiz); /* Returns: number of bytes placed in the buffer, -1 on error */
- symlink create a symbolic link sympath points to the actualpath
- readlink reads the targeted pathname of the given symbolic link path
File Times
| Field | Description | Example | ls(1) option |
|---|---|---|---|
| st_atime | last access time | read | -u |
| st_mtime | last modification time (file content) | write | default |
| st_ctime | last change time (i-node) | chmod, chown | -c |
utime Function
#include <sys/types.h> #include <utime.h> int utime(const char *filename, const struct utimbuf *times); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ struct utimbuf { time_t actime; /* access time */ time_t modtime; /* modification time */ }; #include <sys/time.h> int utimes(const char *filename, const struct timeval times[2]); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ struct timeval { long tv_sec; /* seconds */ long tv_usec; /* microseconds */ };
- Change the access time and modification time of a file
- 如果 times 參數給 NULL,則會被設置為目前時間
0x05 Directory Operations
mkdir and rmdir function
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */ #include <unistd.h> int rmdir(const char *pathname); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */
- mkdir 建立相對應權限的資料夾
- 當使用 rmdir 刪除資料夾時:
- 如果資料夾不是空的,function 會回傳 -1
- 如果資料夾是空的,且沒有 process 正開啟這個資料夾,則資料夾會被刪除並釋放空間
- 如果資料夾是空的,但有 process 正開啟這個資料夾,則資料夾會被刪除但暫時不會釋放空間,此時已經無法再被刪除的資料夾內建立任何檔案,當 process 關閉資料夾後,資料夾便會被釋放
Reading Directories
資料夾的 access 權限:
- Read: must have read and execute permission
- Create/write: must have write and execute permission
#include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> DIR *opendir(const char *name); /* Returns: pointer to the directory if OK, NULL on error */ DIR *fdopendir(int fd);
#include <dirent.h> struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp); /* Returns: pointer to a dirent structure if OK, NULL on reaching EOF or error */ struct dirent { ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ off_t d_off; /* offset to the next dirent */ unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ unsigned char d_type; /* type of file */ char d_name[256]; /* filename */ };
- 一開始會指向資料夾的第一個檔案,每次呼叫readdir就會往後一個檔案
#include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> int closedir(DIR *dirp); /* Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error */
Seek in an Opened Directory
#include <sys/types.h> #include <dirent.h> void rewinddir(DIR *dirp); /* Returns: current location of the opened dir */ long telldir(DIR *dirp); /* Returns: current location of the opened dir */ void seekdir(DIR *dirp, long offset);
- rewinddir: resets the position of the directory stream dirp to the beginning of the directory.
- telldir: returns the current location associated with the directory stream dirp.
- seekdir: set the location(offset) in the directory stream, offset 的起點是目前下個獨進來的點,也就是下一次 readdir 的位置
chdir, fchdir, getcwd
Every process has a current working directory
- The current working directory is inherited from the parent
- The current working directory for each process is independent
#include <unistd.h> int chdir(const char *path); /* Returns: 0 if OK, 1 on error */ int fchdir(int fildes); /* Returns: 0 if OK, 1 on error */ #include <unistd.h> char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size); /* Returns: buf if OK, NULL on error */
- chdir: change working directory
- fchdir: 同 chdir,只是使用 file description 指定檔案
- getcwd: get current working directory
0x06 Device Special Files
每個系統檔案都有他的 major/minor device numbers,編碼後儲存在 system type dev_t
- major number 用於識別 device driver,可以用
major(dev_t) - minor numbers 用於識別 specific sub device,可以用
minor(dev_t)
在前面的 struct stat 中有 st_dev 和 the st_rdev 有什麼差別?
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; struct stat buf; for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) { printf("%s: ", argv[i]); if (stat(argv[i], &buf) < 0) { err_ret("stat error"); continue; } printf("dev=%d/%d", major(buf.st_dev), minor(buf.st_dev)); if (S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode) || S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode)) // 是 character 或是 block { printf(" (%s) rdev = %d/%d", (S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)) ? "character" : "block", major(buf.st_rdev), minor(buf.st_rdev)); } printf("\n"); } exit(0); }
$ ./fig4.25-devrdev / /dev /home/chuang /dev/tty0 /dev/sda2 /: dev = 8/2 /dev: dev = 0/14 /home/chuang: dev = 8/2 /dev/tty0: dev = 0/14 (character) rdev = 4/0 /dev/sda2: dev = 0/14 (block) rdev = 8/2
- Every file has a st_dev number, which indicates the container file system
- Only device files have st_rdev numbers, which indicates the device/sub-device
- mknod command: make block or character special files
Common Device Special Files
- /dev/hdaN? – IDE disks and partitions
- /dev/sdaN? – SCSI or SATA disks and partitions
- /dev/scdN – CD/DVD-ROMs
- /dev/ttyN – terminals
- /dev/ttySN – COM ports
- /dev/pts/N – pseudo terminals
- /dev/null
- /dev/zero
- /dev/random