目錄表
Threads
0x00 Outline
- Introduction
- Thread concepts
- Thread identification
- Thread creation
- Thread termination
- Thread synchronization
0x01 Introduction
- thread 可以在一個 process 執行多個工作
- 在一個 process 中的所有 thread 共享同樣的 process component,如 file descriptor 或 memory
- 而對於在不同 thread 間共享的資源,我們必須有同步機制去避免不同 thread 看到資料內容不一致的問題
0x02 Thread concepts
- 傳統的 UNIX process 可視為 one signal thread,每個 process 一次做一件事
- multiple threads 可以在 signal process 中一次做多個工作
- thread 在一個 process 中共享
- Text of the executable program
- The program’s global and heap memory
- Stacks
- File descriptors
thread 的組成
- thread ID
- Set of register values
- Stack
- Scheduling priority and policy
- Signal mask
- An errno variable
- Thread-specific data
UNIX Thread Standard
- Defined by POSIX
- known as pthreads or POSIX threads
- 寫程式時必須
#include<pthread.h> - 用 gcc 編譯支援 thread 的 C/C++ 程式時,必須加上 -pthread or -lpthread 參數
Linux thread implement
- Linux 上的 thread 是透過 clone system call 實作的
- Linux 上的 thread 有兩大類
- LinuxThreads:
- The original thread implementation on Linux
- NPTL(Native POSIX Thread Library):
- 和 POSIX.1 相容性較高
- 效能較好
- 需要 C library 和 kernel support
- 都是 1:1 mode
- process 中的每個 thread 在 kernel 中都可對應一個 entity,在 CPU schedule 時會分配到個別的資源
0x03 Thread identification
- 每個 thread 都有 thread ID,然而和 pid 不同,thread ID 並不唯一,且只在他所屬的 process 中有意義
- thread ID 可用
pthread_t這個資料型態表示
- 比較 thread 是否相同
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_equal(pthread_t tid1, pthread_t tid2); /* Returns: nonzero if equal, 0 otherwise */
- 取得 thread id
#include <pthread.h> pthread_t pthread_self(void); /*Returns: the thread ID of the calling thread*/
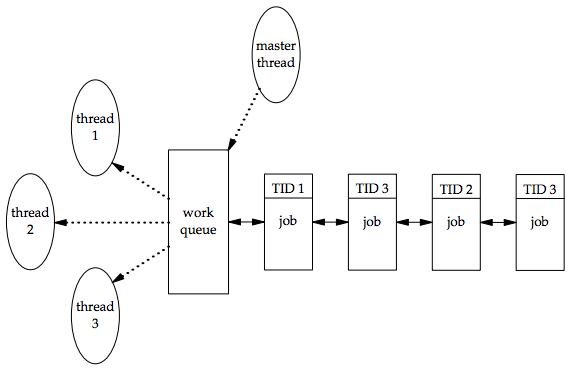
- master thread 可以依照 ID 指派 job 給 worker thread
- worker 可以使用 pthread_equal 和 pthread_self 找出自己負責的 job
0x04 Thread Creation
- 對 pthreads 而言,當程式執行後,相當於跑了一個包含單一 thread 的 process,可以透過以下函式新增 thread
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp, const pthread_attr_t *restrict attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *restrict arg); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- pthread_create 成功的話 tidp 指向 thread id 的 memory 位置,這個可以傳入先前宣告的 pthread_t variable
- attr 可以客製一些 thread 屬性,NULL 為預設
- 新的 thread 建立成功後會執行 start_routine function
- arg 為給 start_routine 的參數
- thread 被建立後,不保證哪一個會先執行
- 新的 thread 可存取原來 process 的 address space,並繼承 calling process 的 floating-point environment(fenv.h) 和 signal mask
#include "apue.h" #include <pthread.h> pthread_t ntid; void printids(const char *s) { pid_t pid; pthread_t tid; pid = getpid(); tid = pthread_self(); printf("%s pid %lu tid %lu (0x%lx)\n", s, (unsigned long)pid, (unsigned long)tid, (unsigned long)tid); } void *thr_fn(void *arg) { printids("new thread: "); return((void *)0); } int main(void) { int err; err = pthread_create(&ntid, NULL, thr_fn, NULL); if (err != 0) { err_exit(err, "can't create thread"); } printids("main thread:"); sleep(1); exit(0); }
$ ./fig11.2-threadid new thread: pid 3207 tid 3084950416 (0xb7e09b90) main thread: pid 3207 tid 3084953264 (0xb7e0a6b0)
- 在不同平台上結果可能不同
- pthread_t 不一定是 integer
- 兩個 thread 呼叫 getpid() 時可能得到不同結果(如 LinuxThreads)
0x05 Thread termination
thread termination
- 終止整個 process
- process 中有任意 thread 呼叫了 exit, _Exit, 或 _exit
- 收到某個 signal 的預設處理方式是 terminating the process
- 終止單一 thread
- 從該 thread 的 start routine function return,return value 即是 thread exit code
- 被同一個 process 中的其他 thread cancel
- thread 呼叫 pthread_exit
thread termination status
#include <pthread.h> void pthread_exit(void *rval_ptr); int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **rval_ptr); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- process 的 exit status 可以透過 wait, waitpid function 取得,thread 的 exit status 我們可以透過 pthread_join 取得
- 假設我們有 A B 兩個執行緒,B 執行緒在做某些事情前需要先等 A 執行緒把事情做完,這時即可使用 pthread_join
- 在 B 執行緒中呼叫 pthread_join function,第一個參數給 A 的 thread id,第二個參數傳入一個 pointer,此時 B 執行緒會在這裡暫停
- 當 A 執行緒呼叫 pthread_exit(void *rval_ptr) 結束時,B 執行緒 pthread_join 中參數 rval_ptr就會指向 exit 參數的 rval_ptr
- 這樣使用 pthread_join 得執行緒就能拿到 exit status 繼續執行了
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- pthread 有 joinable 和 unjoinable 兩種狀態
- 一般預設 pthread create 時 thread 是 joinable 的
- 若 pthread 是 joinable 時,若沒有其他 thread 對他調用 pthread_join,則該 thread 執行 pthread_exit 後,thread id 和 exit status 會保留在記憶體中直到對該執行緒的 pthread_join 被調用,造成記憶體消耗
- 透過 pthread_detach 可將執行緒設為 unjoinable 狀態,此時執行緒在執行 pthread_exit 後,記憶體資源會直接被釋放
- 對 detach thread 調用 pthread_join 會 return EINVL
cancelling a thread
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- pthread_cancel 可以向目標執行緒發送 cancel 請求,然而要怎麼處理這個請求是執行緒自己決定的,pthread_cancel 亦不會等待執行緒回應
cleanup function
#include <pthread.h> void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routine)(void *), void *arg); void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
- 在 thread 結束時我們可以呼叫一些函式做處理,基本上這些 recall function 被存放在 stack 架構中
- 在 thread function 中我們可以用 pthread_cleanup_push function 將之後要調用的函式依序推入堆疊
- 推入 stack 的函式會在幾個時機點被調用
- thread 呼叫 pthread_exit 時
- thread 回應 cancellation request 時
- thread 呼叫 pthread_cleanup_pop 時
- push 和 pop 要兩兩對應,否則會編譯不過
- pop 的 參數 execute 要非零才回執行,否則僅會移除先前推入的 function
comparison process and thread function
| Process | Thread | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fork | pthread_create | create a new flow of control |
| exit | pthread_exit | exit from an existing flow of control |
| waitpid | pthread_join | get exit status from flow of control |
| atexit | pthread_cleanup_push | register function to be called at exit from flow of control |
| getpid | pthread_self | get ID for flow of control |
| abort | pthread_cancel | request abnormal termination of flow of control |
0x06 Thread synchronization
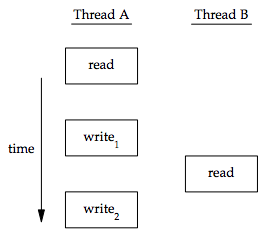
- 同個 process 的 thread 共享同樣的記憶體空間,對於所有 thread 我們必須使他們取得的資料一致
- 上圖若寫入需要花兩個 cycle 而讀取只需一個 cycle,且讀取正好發生在寫入間則產生不一致
- 上圖若兩個執行緒都要增加一個變數,其中涉及三個動作,此也可能產生不一致
- Read the memory location into a register
- Increment the value in the register
- Write the new value back to the memory location
- 為了解決這個問題,我們使用 lock,一次只允許一個執行緒存取變數
Mutexes
- Mutual exclusives 互斥鎖
- 是一個基本的 lock
- 當 thread 存取共享資源前設置一個 lock
- 當存取結束後釋放 (unlock)
- 當 mutex 被設置時,其他嘗試要存取的 thread 會被 block 直到鎖被釋放
- 當有多個執行緒都在等待,鎖被釋放時,最快執行的 thread 取得鎖,其他執行緒則繼續等待
pthread mutexes
- Data type: pthread_mutex_t
initialize and destroy
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr); int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */ pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
lock and unlock
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- 以下範例我們在增加、減少、確認變數 f_count 前都先執行 lock 將他上鎖
#include <stdlib.h> #include <pthread.h> struct foo { int f_count; pthread_mutex_t f_lock; int f_id; /* ... more stuff here ... */ }; struct foo *foo_alloc(int id) /* allocate the object */ { struct foo *fp; if ((fp = malloc(sizeof(struct foo))) != NULL) { fp->f_count = 1; fp->f_id = id; if (pthread_mutex_init(&fp->f_lock, NULL) != 0) { free(fp); return(NULL); } /* ... continue initialization ... */ } return(fp); } void foo_hold(struct foo *fp) /* add a reference to the object */ { pthread_mutex_lock(&fp->f_lock); fp->f_count++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock); } void foo_rele(struct foo *fp) /* release a reference to the object */ { pthread_mutex_lock(&fp->f_lock); /* last reference */ if (--fp->f_count == 0) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock); pthread_mutex_destroy(&fp->f_lock); free(fp); } else { pthread_mutex_unlock(&fp->f_lock); } }
deadlock avoidance
- 會形成 deadlock 的情況
- 重複對同個 mutex 上鎖
- 兩個 thread(T1/T2),兩個 metux(Ma/Mb),T1 依序上鎖 Ma,Mb,T2 依次上鎖 Mb,Ma,則形成 T1,T2 互等死結
- 解決方式
- 第一種容易避免,或使用 PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE 即可
- 第二種可以對 metux 要求上鎖順序
- 或是可以使用 pthread_mutex_trylock function
Reader-Writer lock
- mutex 只有 lock/unlock 兩種操作
- rwlock 可以
- Locked in read mode
- Locked in write mode
- Unlocked
- rwlock 在同時間允許多個 read lock
- rwlock 一次只允許一個 write lock
- read lock 和 write lock 彼此互斥,若對方已經先 lock,則後到者必須等待
pthread Reader-Writer Lock
- Data type: pthread_rwlock_t
initialize and destroy
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr); int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
lock and unlock
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t*rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t*rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t*rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t*rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t*rwlock); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
Condition Variable
- pthread_join 解決了多個執行緒在等待一個執行緒結束的通知
- 而若我們要的不是執行緒的結束,而是完成某項工作後的通知,我們可以用 condition variable 處理
- condition variable 必須要和 mutex 合併使用
pthread condition variable
- Data type: pthread_cond_t
initialize and destroy
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond); int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */ pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
wait for the condition
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
- 在執行緒呼叫 pthread_cond_wait 前要先申請 mutex,當 thread 通過 pthread_cond_wait 進入 waiting 狀態時會先釋放 mutex
- 而當條件滿足而離開 pthread_cond_wait 前,會再對 metux 上鎖一次,所以呼叫 pthread_cond_wait 前後的 lock/unlock 會互相對應
#include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> static pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; struct node { int n_number; struct node *n_next; } *head = NULL; /* thread_func */ static void cleanup_handler(void *arg) { printf("Cleanup handler of second thread./n"); free(arg); (void)pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); } static void *thread_func(void *arg) { struct node *p = NULL; pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup_handler, p); while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); // pthread_cond_wait里的线程可能会被意外唤醒,如果这个时候head != NULL,则不是我们想要的情况。这个时候,应该让线程继续进入pthread_cond_wait while (head == NULL) { pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mtx); /* pthread_cond_wait 會先解除之前的 pthread_mutex_lock 鎖定的 mtx,然後 block 在 queue 休眠,直到再次被喚醒 多數情况下是等待的條件成立而被唤醒,唤醒後,該執行緒會先執行 pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); 再讀取资源 */ } p = head; head = head->n_next; printf("Got %d from front of queue/n", p->n_number); free(p); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); // 釋放互斥鎖 } pthread_cleanup_pop(0); return 0; } int main(void) { pthread_t tid; int i; struct node *p; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); /*[tx6-main]*/ for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { p = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); p->n_number = i; pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); // 需要操作head这个臨界資源,先上鎖, p->n_next = head; head = p; pthread_cond_signal(&cond); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); // 解鎖 sleep(1); } printf("thread 1 wanna end the line.So cancel thread 2./n"); pthread_cancel(tid); // pthread_cancel 是從外部终止子執行緒,子執行緒會在最近的取消點退出執行緒,而在我们的程式中,最近的取消點為 pthread_cond_wait() pthread_join(tid, NULL); printf("All done -- exiting/n"); return 0; }
timed wait
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime); struct timespec { __time_t tv_sec; /* Seconds. */ long int tv_nsec; /* Nanoseconds. */ };
- 等待至特定時間若條件不滿足則放棄等待,此時 pthread_cond_timedwait 會回傳 ETIMEDOUT
void maketimeout(struct timespec *tsp, long minutes) { struct timeval now; /* get the current time */ gettimeofday(&now); tsp->tv_sec = now.tv_sec; tsp->tv_nsec = now.tv_usec * 1000; /* usec to nsec */ tsp->tv_sec += minutes * 60; /* add the offset to get timeout value */ }
notifications
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond); /* Returns: 0 if OK, error number on failure */
- broadcast 會喚醒所有在等待的執行緒
- signal 會喚醒等待中的一個執行緒
Barriers
- 可以理解成一個 mile stone,當一個執行緒率先跑到 mile stone 的時候就先等待,其他執行緒都到位之后,再從等待狀態喚醒,繼續做後面的事情
- 當 pthread_barrier_wait 再成功喚醒後會回傳 PTHREAD_BARRIER_SERIAL_THREAD 給隨機一個 thread,其他則回傳 0,錯誤則回傳 error number
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_barrier_destroy(pthread_barrier_t *barrier); int pthread_barrier_init(pthread_barrier_t *restrict barrier, const pthread_barrierattr_t *restrict attr, unsigned count); int pthread_barrier_wait(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);